Tuberculosis (TB) of the lungs is a transmittable infection caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis can spread to other parts of the body including the brain and spine. Tuberculosis has been a leading cause of death all around the world; however today most patients are cured with antibiotics. It takes a long time to heal tuberculosis and a person may have to take medications for up to 6-9 months or more.
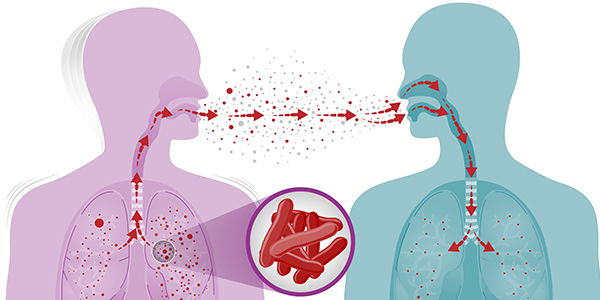
Tuberculosis can be spread through the air, it spreads when we breathe in the released germs and we can get infected. Though tuberculosis is transmittable, it is not that easy to catch it. The germs usually grow very slowly. Sometimes when we spend a lot of our time with the person who has TB, those germs grow a little early than usual, that’s how it spreads among co-workers, friends, or family members. The germs that cause tuberculosis don’t multiply on surfaces, therefore you cannot get the disease by shaking hands with somebody who has it or by sharing what they eat or drink.
A healthy body with a good immune system may fight tuberculosis bacteria. However, if you have HIV or AIDS, diabetes, kidney disease, neck or head cancer, if you’re taking chemotherapy or medications for organ transplants or certain drugs that are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, or psoriasis and if you have low body weight or malnutrition then the chances of being infected are more.
If you have tuberculosis of the lungs you have symptoms like chest pain, coughing for up to 3 weeks, coughing which produces blood, sweating at night, chills, fever, and you feel tired all the time. Loss of appetite and loss of a lot of weight is also known to happen. And if you experience any of these, visit your doctor and get yourself tested. Also in case of chest pain immediately get medical help.
When you visit the doctor, they will ask you to conduct a physical exam to check if you have any fluid in your lungs and to check the overall condition of the body. They may also ask you for your medical history. Other than these, the doctor will ask you to take a few laboratory tests such as:
- Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST): This laboratory test is performed by inserting a small amount of fluid named tuberculin into the skin in the lower part of the arm. A reaction on the arm is read within 48-72 hours. Values of reaction which cause swelling or induration of more than 10mm are considered reactive and are indicators of tuberculosis infection
- Complete blood count with ESR- The complete blood count gives an indication of the severity of the infection. The ESR is normally high in patients with tuberculosis
- Chest radiograph: This laboratory test is taken to check for any chest abnormalities. Lesions can occur anywhere inside the lungs and may vary in shape, density, size, and cavitations.
- Sputum for AFB: the tubercular bacilli are acid fast. Hence sputum is stained and examined for acid fast bacilli. The presence of acid fast bacilli is highly suggestive of tuberculosis
- Sputum culture: the sputum is cultured for routine culture and T.B culture. This confirms the presence of T.B in the lungs
- Drug resistance: This is a very important test for all patients as it is very crucial to identify drug resistance before time to ensure treatment is effective.
- PCR for Tuberculosis: This test is a very specific and sensitive test and uses a molecular technique to detect tuberculosis.
- Gene Xpert is another test that can tell the resistance of the bacteria to rifampicin a commonly used anti-tubercular medicine
- Gold interferon or gamma interferon: this test is done many a time to detect latent tuberculosis or hidden tuberculosis
- Pleural Fluid Examination: fluid taken from the pleural spare outside the lump is investigated for tuberculosis most people with tuberculosis have high protein in pleural fluid and a high number of lymphocytes in the microscopic examination. The pleural fluid can also be examined for PCR, gene Xpert, culture, drug resistance, and AFB bacteria
- CT scan: This laboratory test is taken for a detailed image of the lungs to check for any signs of infection
- Bronchoscope: This Laboratory test is a procedure in which a scope is inserted through your mouth or nose to see your lungs and the air passages clearly
- Thoracentesis: This laboratory test is a procedure where the fluids are removed from the space between our lungs and the wall of our chest.
- Lung biopsy: This laboratory test is a procedure to take a sample of our lung tissue and examine it under a microscope.
If you are suffering from tuberculosis of the lungs then avoid getting in close contact with others, take a rest until your doctor gives you the clearance that you are no longer contagious, and if you can resume your normal routine.