With the onset of the winter season, it is the season for respiratory tract allergies and lung infections. In view of the alarming air pollution levels and the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic caused by The SarsCov-2 virus (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome), it is essential to be mindful of all the symptoms and follow the mandatory precautionary measures of wearing a mask, hand sanitizing and maintaining social distancing protocols.
Lung infections can be broadly divided into 2 groups:
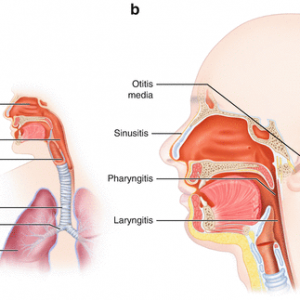
- Upper respiratory tract infections affect the nose, throat (pharyngitis and laryngitis), ears, and sinus. Symptoms of common cold and mild flu, sore throat, headache, earache, blocked sinuses, runny nose, sneezing, body ache, and fever may be present.
- Lower respiratory tract infections affect the respiratory airways and lungs and are caused by viruses (severe flu, pneumonia) and bacteria (tuberculosis). Labored breathing, shortness of breath, fever, severe phlegmy cough, wheezing, and tightness in the chest are some of the symptoms.
Common cold
Common colds can be caused by over 250 different types of viruses, but most commonly it is caused by the adenovirus and is contagious for many days after recovery and is, therefore, contagious. Typical symptoms include runny nose, headache, sore throat, and frequent sneezing.
Influenza (flu)
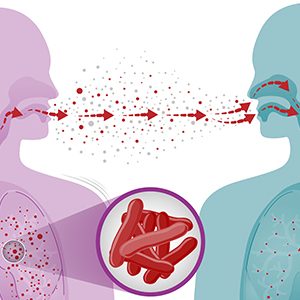
Caused by Influenza A and B virus among children and adults, it is highly contagious and spreads by contact with an infected person’s sputum droplets while talking and sneezing. Typical symptoms are fever, sore throat, headache, body ache, chills, runny nose, blocked sinus, vomiting, and diarrhea. Severe flu symptoms could trigger asthma attacks, and worsen pre-existing medical conditions like diabetes and heart disease.
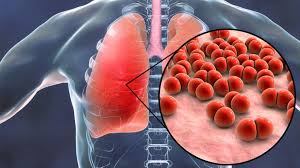
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is caused by both, bacterial and viral (influenza A and B, adenovirus, parainfluenza, and RSV) infections. It affects the lungs and is characterized by symptoms of fever, cough with thick mucus, wheezing, chills, headache, body ache, and tiredness. Bacterial pneumonia is not as contagious as viral pneumonia. The elderly and children are more vulnerable to viral pneumonia, as it can be life-threatening for them.
Swine Flu (H1N1)
Caused by the Influenza-A virus, it has a genetic similarity to viruses found in pigs and can survive in animals like monkeys, dogs and cats, and livestock, among others. The most contagious period is the first 1-7 days and spreads through kissing, sputum flecks while sneezing, or proximity to livestock or pig barns. It does not spread by eating pork. Symptoms include fever, chills, headache, body ache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sore throat, pain while swallowing, and painful joints. It can be prevented by taking the swine flu vaccine.
Avian flu (Bird flu)
Also caused by the Influenza-A virus variants (H7N9, H5N1) infecting birds, it spreads to humans through infected birds and their droppings, exposure to infected bird coops or aviaries, or coming into contact with an infected person. It is characterized by fever, diarrhea, breathing difficulties, headache, body ache, runny nose, and sore throat. It can be seriously life-threatening and 40% of people infected with the H7N9 variant and 50% of people infected with the H5N1 variant die of complications.
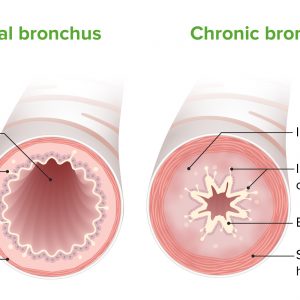
Bronchitis
Bronchitis occurs when the air passages (bronchi) become inflamed due to infection. It is characterized by constant coughing fits (with mucus), sore throat, watery eyes, body ache, and headache. Smoking and breathing in polluted air and dust allergies aggravate the symptoms.
Tuberculosis (TB)
Caused by the bacteria mycobacterium tuberculosis, it spreads from coming into contact with an infected person’s sputum droplets while coughing or sneezing and becomes airborne. Every 4th person in the world is infected with TB germs (25% of the world’s population): which means that the infection can remain latent for months before it is finally diagnosed. It is completely treatable, but those with low immunity, HIV-positive patients (they have a 20 times higher risk of TB as compared to others), malnourished people, diabetics, and excess alcohol drinkers and smokers are at higher risk and need to be more cautious. Weight loss, cough with mucus, fever, and night sweats are the prominent symptoms, which may be mild, thus overlooking getting diagnosed. There are Multi Drug Resistant strains of TB that are more difficult to treat.