A pregnancy lasts up to 40 weeks and these weeks are grouped into three different trimesters. The second trimester is 13-27 weeks of pregnancy. By the second trimester, the baby grows larger in size and becomes stronger. Most women think the second trimester is easier than the first but it’s important to be informed about the pregnancy during the second trimester as well. The more you understand about your pregnancy, week after week, the more it helps you make informed decisions and help you with the big changes coming ahead.
During the second trimester of your pregnancy, the symptoms that you may have had during the first trimester begin to improve. However, you may see other changes or symptoms, like dizziness due to low blood pressure, body aches, the uterus expanding a little, increased appetite, and stretch marks on the stomach, breast, thighs, or buttocks, you may also feel the baby moving, swelling of ankles or hands, or you may even see skin changes like darkening of the skin around your nipple, or see patches of darker skin. See the doctor immediately if you experience symptoms like vomiting, extreme swelling, nausea, rapid weight gain, or yellowing of the white of the eyes as it may be jaundice.
By now we know that the baby’s organs become fully developed in the second trimester, so the baby can hear and swallow. The baby also begins to move around later on in the second trimester. The baby also develops a sleeping and waking cycle that the pregnant lady will begin to notice.
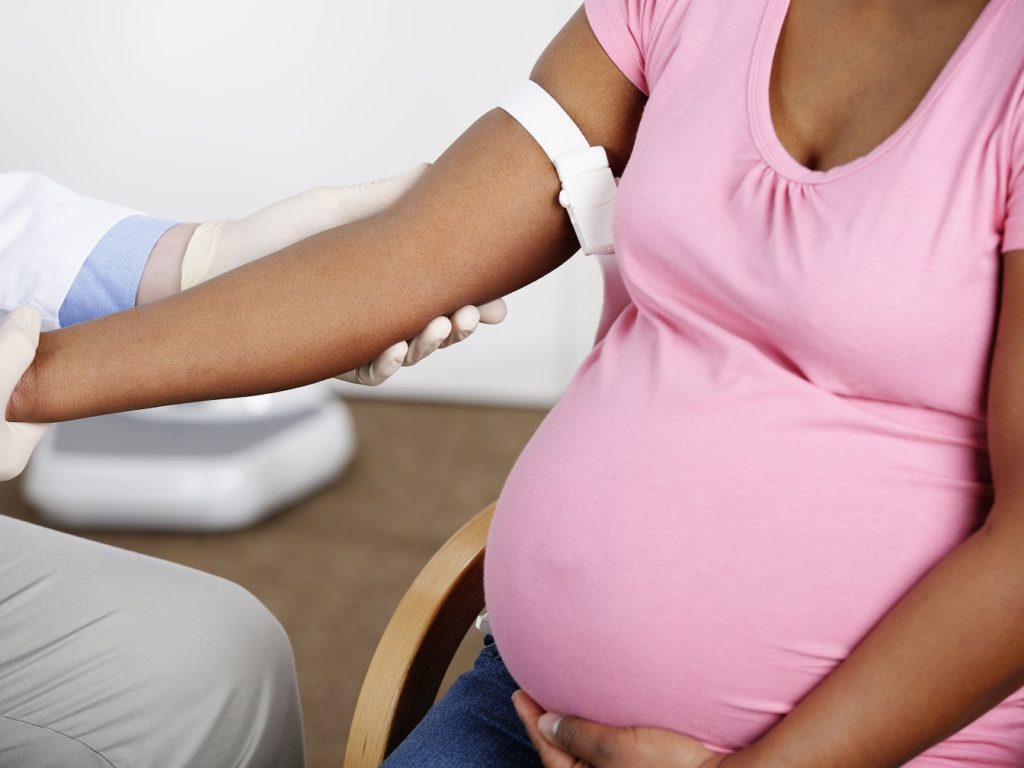
During the second trimester, your doctor will suggest you perform some laboratory tests also known as second trimester tests, these tests will include weight checkups, ultrasound, diabetes screening with blood tests, birth defect and other genetic screening tests, measuring your blood pressure, etc.
These lab tests or second trimester screening is important because:
- Blood test: This lab test are done to check blood group and blood type, if your blood is Rh negative or if your partner’s blood is Rh positive, develop, antibodies that may prove dangerous to your fetus. This can be prevented with the help of an injection given in the 28th week of your pregnancy. The blood test also looks for anemia, HIV, hepatitis B, syphilis, chickenpox, cystic fibrosis, spinal muscular atrophy etc. Your doctor will suggest you to get blood tests regularly even if there is no family history for these disorders.
- Multiple marker tests: This lab test is done to check for neural tube defect such as spinal bifida and chromosomal disorders. The results of these tests are combined with the first trimester screening to give more accurate results also known as integrated screening test. This test is taken usually between the 15th weeks to 20th week of pregnancy These tests include LFP, BHCG, Free estriol and Inhibin.
- Ultrasound: This lab test is the safest and painless test as it uses the sound waves to make the images revealing the baby’s shape and position inside the uterus. Ultrasounds done between 18-20 weeks are also called second trimester ultrasounds or level 2 ultrasounds. It also confirms that the baby is developing normally. If a woman is at a higher risk pregnancy, then she may have to get multiple ultrasounds in their second trimester.
- Glucose screening: This lab test is taken to check for gestational diabetes that may develop in some women during the pregnancy. It can cause health problems for the baby if not diagnosed or treated. This lab test is taken during 24-28 week of the pregnancy, but this test can be taken early if the woman is at higher risk for having diabetes.
- PUBS (Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling): This lab test is also known as cordocentesis or fetal blood sampling or umbilical vein sampling. It examines the fetal blood directly from the umbilical cord to detect any disorders. This test is taken after 18 weeks of pregnancy. This test is used when amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling results are not conclusive.
- Amniocentesis: This lab test is taken to take the sample of the amniotic fluid that surrounds the fetus. This test checks for the signs of chromosomal disorders or genetic problems or neural tube defects. This test is also taken in between the 15-20 week of pregnancy.
- Other Tests: Other lab tests may be taken during the pregnancy to check for thyroid, hepatitis C, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, CMV also known as cytomegalovirus, fragile x syndrome, tay-sachs disease, etc. Before you take any other tests consult your doctor.
Other than these, the doctor may also tell you to get your urine tested along with weight and blood pressure regularly, until the time you deliver. These tests can find any conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure (preeclampsia). Also to decide which tests are correct for you, consult your doctor and don’t hesitate to ask them why the test is needed, what are the risks or benefits of those tests and what the results may tell you or can’t tell you.