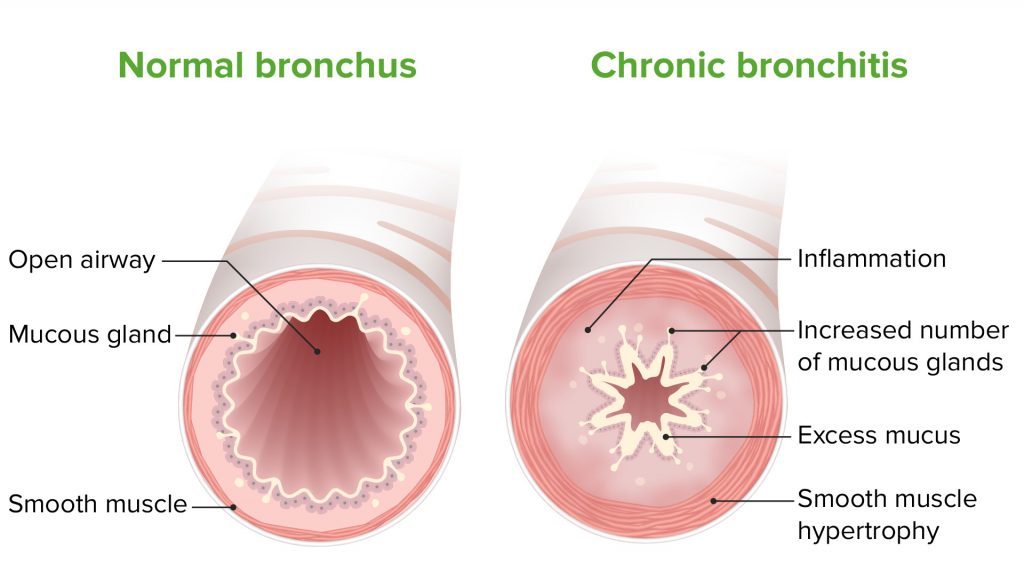
When there is irritation of the lining of your bronchial tubes that carry air back and forth from your lungs, it’s called bronchitis generally people who have bronchitis, cough up thick mucus, which can be discolored. The irritations on the lining of the bronchial tubes are caused to due various viruses such as flu and some bacteria.
Bronchitis may possibly be either acute or chronic. If recently you have had a cold that may have turned into a cough then you might have an acute bronchitis whereas if your cough is producing persistent mucus that lasts longer than 3 months or more then it might be chronic bronchitis. Acute bronchitis is a shorter illness that may be known as a cold or viral infection that lasts only for a few days whereas Chronic bronchitis may last for months every year and causes difficulty in breathing and the symptoms may get worse during that time. Also if chronic bronchitis occurs with emphysema, it becomes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and you may need medical attention immediately.
Symptoms for both acute and chronic bronchitis include coughing, repetition in the production of sputum (mucus) which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color speckled with blood creating shortness of breath, chest discomfort, constant fever, and chills. In case of acute bronchitis, you may have only cold symptoms such as headaches, and body aches, these symptoms will improve in a week or so and you may get a cough that will vanish in a few weeks whereas chronic bronchitis may cause a cough lasting at least 3 months with repetitive bouts occurring for two following years. Also when your cough gets worse, at those times you may have acute bronchitis plus chronic bronchitis.
The causes of acute bronchitis may be the some viruses that cause cold and flu whereas the most common cause of chronic bronchitis is smoking cigarettes, air pollution, dust, etc. People who smoke have a higher risk of bronchitis than people who don’t smoke. Adults or young children, all have a greater openness to these infections. Sometimes the work environment is also a cause of such diseases. If an adult is working in chemical industries where they are exposed to chemical fumes, they have a greater risk than others to have bronchitis. Some people also suffer from gastric reflux; repeated heartburns can cause irritation to the throat making an individual prone to developing bronchitis.
Visit the doctor in case the cough is longer than 3 weeks, if the cough does not let you sleep, if the fever is high and is not coming down, If the thickened mucus is clear or contains blood, and most important if the cough causes difficulty in breathing.
Your doctor may recommend you to take rest and drink lots of water as it helps an acute bronchitis fade away more quickly. Other treatments may include a cough syrup in case you’re not producing anymore mucus but if you’re still clearing your airways then the doctor might not recommend you to take it, a pain reliever, the doctor may also suggest you sit in a steamy bathroom and may also ask you to take bronchodilators (inhaled medications that help you open up airways)
Your doctor may also advise you to take these laboratory tests:
- Sputum Culture
- Siprometry
- Chest X-ray
These laboratory tests are important because:
- If your symptoms are severe, the doctor may ask for sputum culture test which your mucus sample you cough up as the lab test will reveal whether the mucus that you are coughing up is caused by an allergy or a whooping cough (pertussis: a contagious bacterial infection). Severe symptoms may need more tests.
- A laboratory tests such a siprometry which is a test of lung function, it measures the air your lungs can hold and how fast it can blow it out. This test helps your doctor find out whether you have asthma in particular or any other breathing problems along with bronchitis
- A laboratory test such as chest x-ray is important in case you had fever because that will confirm if whether you have pneumonia or not.
- In some cases PCR for H1N1 ( Swine flu) may be required, investigation for tuberculosis may also be done such as a sputum for AFB, PCR for TB and TB culture
Bronchitis can be prevented if you follow these tips:
- Avoid smoking as it increases the risk of chronic bronchitis
- Check if you are vaccinated for influenza. Get a yearly flu vaccine to help you protect from the flu. Consider vaccines that protect against some types of pneumonia.
- Wash your hands regularly to reduce the risk of catching a virus. Try using alcohol-based hand sanitizers as frequently as possible.
- In case you have been diagnosed with COPD, then consider wearing a face mask to avoid getting exposed to fumes or dust when you are in a crowded place or while traveling.