Dengue Fever is a very serious public health problem faced by the whole world but more so by countries like India and many African.
It is a mosquito borne disease caused by Flavivirus.

The mosquito spreading dengue is Aedes Aegypti.
This mosquito bites primarily in the day and mainly two hours after sunrise and many hours before sunset.
Only female mosquitoes bite in order to lay eggs.
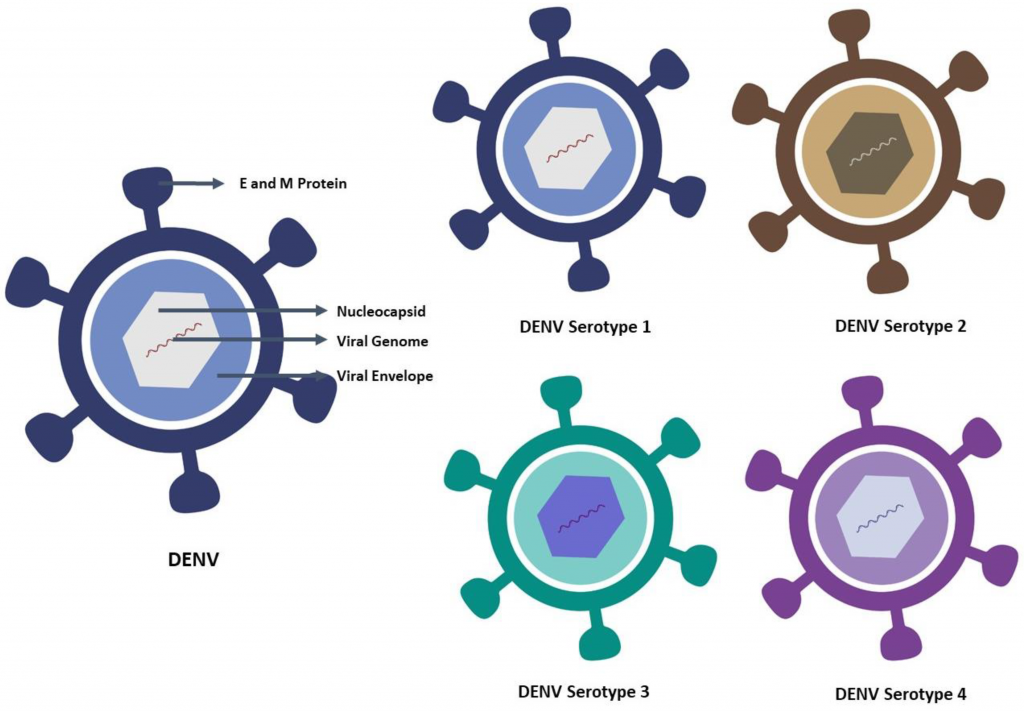
Dengue virus is of 4 serotypes and another fifth serotype has been recently detected.
The incubation period is from 5-7 days and the symptoms vary from mild disease to severe Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever (DHF) and Dengue Shock Syndrome (DSS).
There are two theories for the occurrence of the severe form of dengue -DSS and DHF. Some believe that the dengue hemorrhagic fever is caused by a virulent strain of the virus while the other theory says that this is because of an exaggerated immune response.
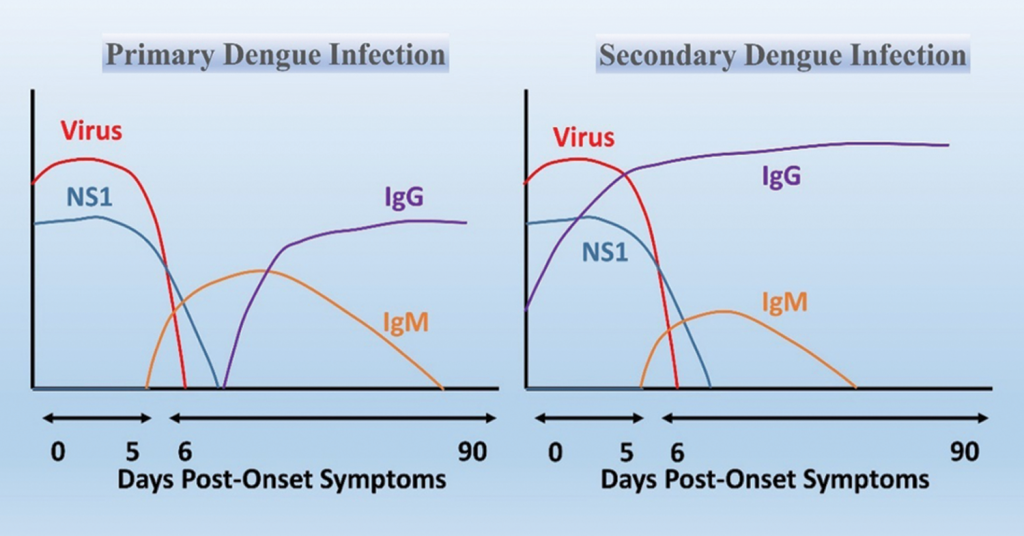
When there is a Primary Infection with dengue, antibodies are produced that lack neutralizing activity. At the time of secondary infection with another serotype the virus and the antibodies produced earlier form virus – antibody complex. This is followed by a mechanism called antibody dependent enhancement where there is an increase in the cells that get infected. This leads to an exaggerated inflammatory response leading to shock syndrome.
Once a person suffers from dengue fever he is immune to that strain of the virus but can be infected by other strains and serotypes. This is called Secondary Dengue and this is more severe.
Secondary Dengue is more severe as it evokes a more severe immunological response in the body and causes Shock Syndrome and Hemorrhagic Fever.