Zinc is an essential micronutrient that plays a fundamental role in maintaining good health of our immune system, skin, gastrointestinal tract and nerves. It is required for many enzymatic reactions in our body. It helps our immune system to prevent disease and fight infection and heal wounds quickly. It strengthens the functioning of brain by aiding in memory, sensory messaging and cognition. It also helps in maintaining hormonal balance, fertility and proper fetal development. Its antioxidant properties help in fighting free radical damage and slowing aging as well as fighting cancer and heart disease. Though required in small quantities, its participation in all key processes of the human body makes it an essential trace element.
Inadequate dietary intake is the most common cause of zinc deficiency. Children, pregnant and lactating mothers are the most frequently affected groups due to increased demands. In children, deprivation of breastmilk and diarrhoea results in huge losses of zinc. Consequently, it may lead to growth retardation, stunting, intellectual disability and immune suppression, makes them prone to getting infections. World Health Organization estimates that 800,000 people die annually due to zinc deficiency, and more than 50% of these are children under the age of five. Poor absorption and increased loss are the other reasons for zinc depletion in the body. High phytates in Asian diet (cereals and legumes) bind to zinc in the food and restricts its absorption. Increased alcohol intake also causes zinc deficiency by increasing its loss from the body.
The clinical presentation of zinc deficiency comprises alopecia (hair loss), dermatitis and acne in skin. Altered cognitive functions lead to poor memory, behavioural abnormalities, psychological disorders, irritability and depression. Hormonal imbalance may result in delayed puberty, infertility and diabetes. Changes in appetite, ability to taste and smell, delayed wound healing and digestive problems may also occur.
Depleted levels of zinc in the blood can be detected by a simple blood test. Excess copper and iron levels in blood may also interfere with zinc uptake, hence their levels may also be checked in relevant scenario.
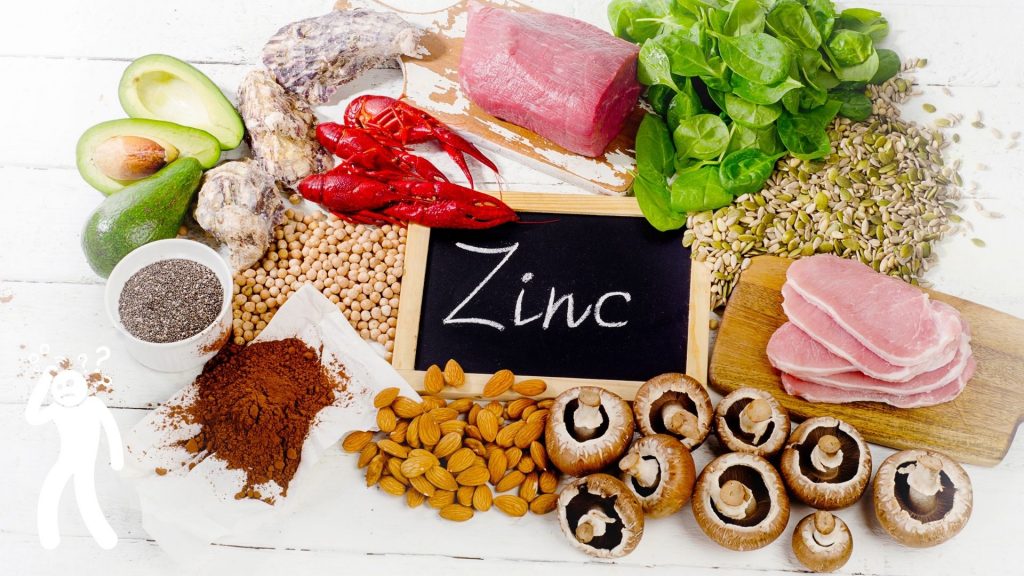
Treatment and prevention of zinc deficiency, both begin with consuming foods rich in zinc. Oysters and red meat are the richest sources of zinc. For vegetarians too, the options are many and include chickpeas, cashews, almonds, yoghurt, eggs, mushrooms and pumpkin seeds. Apart from diet, zinc supplementation in the form of multivitamins and zinc fortified foods are also available. Women in the reproductive age group should take special care as zinc is required for proper fetal development. For children suffering from chronic diarrhoea, zinc supplementation can tremendously improve their health and immunity.